
Kód: 08286969
Computer Investigation of a Lobed-Mixer Fuel-Injection Strut in a Scramjet Engine Model
Autor Thong Q Dang
A method of enhancing fuel/air mixing using streamwise vorticity for scramjet applications is presented. The generation of large-scale streamwise vortices is achieved by the incorporation of a lobed-mixer device into the fuel-inje ... celý popis
- Jazyk:
 Angličtina
Angličtina - Vazba: Brožovaná
- Počet stran: 102
Nakladatelství: Biblioscholar, 2013
- Více informací o knize

Mohlo by se vám také líbit
Darujte tuto knihu ještě dnes
- Objednejte knihu a zvolte Zaslat jako dárek.
- Obratem obdržíte darovací poukaz na knihu, který můžete ihned předat obdarovanému.
- Knihu zašleme na adresu obdarovaného, o nic se nestaráte.
Více informací o knize Computer Investigation of a Lobed-Mixer Fuel-Injection Strut in a Scramjet Engine Model
Nákupem získáte 165 bodů
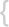 Anotace knihy
Anotace knihy
A method of enhancing fuel/air mixing using streamwise vorticity for scramjet applications is presented. The generation of large-scale streamwise vortices is achieved by the incorporation of a lobed-mixer device into the fuel-injection struts of a proposed NASA scramjet engine. Conceptually, the lobed-mixer strut design is a three-dimensional lifting surface with a sinusoidal spanwise lift distribution. In the flow passage between the strut leading- and trailing-edges, the presence of a spanwise pressure gradient generates secondary flows. In the region behind the strut, which is a lifting surface, the shed vorticity system consists of periodic large-scale counter-rotating streamwise vortices. To evaluate this hypermixer concept, CFD calculations were carried out at supersonic combustor inlet Mach numbers ranging from 2 to 3 for cold flows. This concept is first analyzed for a 3D cascade of struts in inviscid flows. Results from this preliminary work reveal that significant secondary flows are generated in and behind the strut regions, while the additional shock losses associated with the lobed strut is small. Results confirm that the mechanism of generating streamwise vorticity is an inviscid phenomenon; the shed vorticity (i.e. streamwise vorticity) behind the strut is proportional to the pressure loading along the strut (Kutta-Joukowsky theorem). The next stage of this investigation considers the effects of viscosity on the generation of streamwise vorticity (or secondary flow). The geometry considered is a single lobed strut with "slip" side walls. Here, the NASA Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes LARCK code (Langley Algorithm for Research in Chemical Kinetics) was used. Relative to the inviscid-flow results, in the absence of flow separation, viscous effects introduce blockage into the flow passage, causing a small reduction in pressure loading and hence a slight reduction in secondary flow.
 Parametry knihy
Parametry knihy
Zařazení knihy Knihy v angličtině Society & social sciences Education
1646 Kč
- Plný název: Computer Investigation of a Lobed-Mixer Fuel-Injection Strut in a Scramjet Engine Model
- Autor: Thong Q Dang
- Jazyk:
 Angličtina
Angličtina - Vazba: Brožovaná
- Počet stran: 102
- EAN: 9781288910380
- ISBN: 9781288910380
- ID: 08286969
- Nakladatelství: Biblioscholar
- Hmotnost: 195 g
- Rozměry: 246 × 189 × 5 mm
- Datum vydání: 01. March 2013
Oblíbené z jiného soudku
-

Oxford IB Diploma Programme: IB Economics Course Book
1607 Kč -

Cambridge IGCSE (R) & O Level Complete Physics: Student Book Fourth Edition
929 Kč -

Cambridge IGCSE (R) & O Level Complete Chemistry: Student Book Fourth Edition
992 Kč -

Physics for You
1249 Kč -

Business Partner B1+ Workbook
462 Kč -

Speed and Accuracy: Multiplication
228 Kč -

Powerful Teaching: Unleash the Science of Learning
665 Kč -

Speed and Accuracy: Division
208 Kč -

Read Write Inc. Phonics: Red Ditty Book Bag Books (Mixed Pack of 10)
1955 Kč -

Dancing Heads
368 Kč -

Freiarbeitsmaterial für die Grundschule - Deutsch - Klasse 1/2
604 Kč -

Business Partner B1 Workbook
434 Kč -

Business Partner B2 Workbook
462 Kč -

Blue Book of Grammar and Punctuation: An Easy- to-Use Guide with Clear Rules, Real-World Examples , and Reproducible Quizzes, Twelfth Edition
393 Kč -

OET Preparation
246 Kč -

KS3 Maths 10-Minute Weekly Workouts - Year 7
199 Kč -

OET Reading Subtest Preparation
343 Kč -

Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths AQA Revision Question Cards - Higher
242 Kč -

Oxford IB Diploma Programme: IB Theory of Knowledge Course Book
1479 Kč -

Positive Discipline Tools for Teachers
429 Kč -

Embodied Teen
545 Kč -

1000 TRIOS or gapped sentences for Cambridge Advanced and Proficiency Exams
608 Kč -

Pearson Edexcel AS and A level Mathematics Statistics & Mechanics Year 1/AS Textbook + e-book
469 Kč -

(ISC) SSCP SG & SSCP Practice Test Kit, 3e
1745 Kč -

Motivation and Reinforcement
1161 Kč -

Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) English Language B Student Book
1328 Kč -

GCSE Spanish Exam Practice Workbook (includes Answers & Free Online Audio)
220 Kč -

Imagine If...
306 Kč -

Vertical Academy
919 Kč -

Oxford International Primary Maths Second Edition: Practice Book 1
323 Kč -

Vol 2 Blackletter Lettering Adventures
635 Kč -

AS & A Level Maths For Dummies
457 Kč -

Forensic Linguistics Articles
417 Kč -

CompTIA Security+ Review Guide - Exam SY0-601
621 Kč -

Abolition of Man
468 Kč -

Human Landscapes from My Country
658 Kč -

Corrected Squares of The Book of Abramelin
14513 Kč -

Hanbo Jutsu: Use of Hanbo, Cane and Walking Stick for Self Defense
284 Kč -

Reading Mind - A Cognitive Approach to Understanding How the Mind Reads
556 Kč -

KS3 Maths 10-Minute Weekly Workouts - Year 8
199 Kč -

Exam Prep for Microeconomics by Pindyck & Rubinfeld, 6th Ed.
1089 Kč -

North Korea's Military Threat
698 Kč -

Ganzheitliche Sprachförderung
807 Kč -

English Language & Literature WORKBOOK: York Notes for GCSE (9-1)
237 Kč -

Release Your Inner Drive
403 Kč -

Effect of Registration Errors on Tracking in a Networked Radar System
1646 Kč -

Princeton Review SAT Premium Prep, 2021
1134 Kč -

CEH v11 Certified Ethical Hacker Study Guide + Practice Tests Set
1872 Kč -

10 Practice Tests for the SAT, 2021 Edition
839 Kč
Osobní odběr Praha, Brno a 12903 dalších
Copyright ©2008-24 nejlevnejsi-knihy.cz Všechna práva vyhrazenaSoukromíCookies







 Vrácení do měsíce
Vrácení do měsíce 571 999 099 (8-15.30h)
571 999 099 (8-15.30h)